How does OpenHands assist with code refactoring, migration, and troubleshooting?
OpenHands aids in code refactoring, migration, and troubleshooting by autonomously navigating and modifying codebases. Its capabilities allows it to perform these tasks seamlessly, efficiently identifying dependencies and workflows, thereby reducing the load on human developers and the duration of the debugging cycle.
What types of tasks can OpenHands perform autonomously?
OpenHands can perform a range of tasks autonomously. It can refactor code, manage migration processes, troubleshoot issues within a codebase, and test changes. Furthermore, it can autonomously navigate and modify codebases, making it an ideal solution for the automation of repetitive tasks.
How does OpenHands integrate with the work of human developers?
OpenHands is designed to work in tandem with human developers, supplementing their work and increasing overall productivity. It accomplishes this by taking over tasks that are repetitive or time-consuming such as code refactoring, migration, and troubleshooting, enabling the human developers to focus on more complex tasks. Thanks to its ability to understand and respond to natural language instructions, developers can interact with OpenHands as they would with a human colleague.
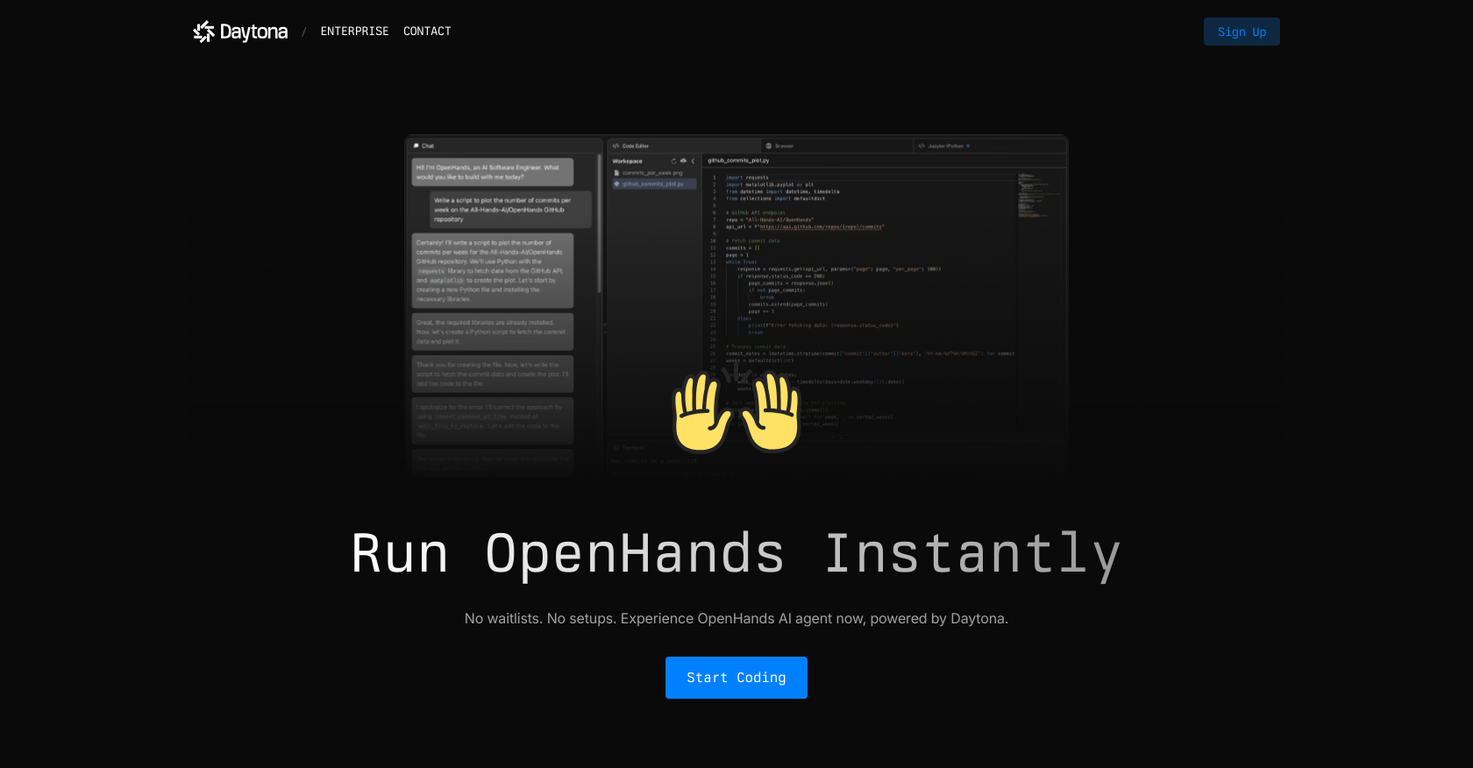
What does it mean that OpenHands provides an integrated workspace?
An integrated workspace in OpenHands means that all the essential tools for end-to-end work are located within a single unified space. This environment includes an embedded shell, a web browser, an editor, and a task planner. The consolidation of these tools within one workspace simplifies workflow, reduces setup time for new tasks and eliminates the need to switch between different environments.
How can non-technical users benefit from OpenHands?
Non-technical users can interact with OpenHands using natural language instructions. This makes it possible for such users to assign tasks, get updates, and otherwise utilize the platform without requiring in-depth technical knowledge. The natural language capabilities of OpenHands make AI accessible to a broader range of users than would be possible with a more technical interface.
What is the role of Daytona in OpenHands' functionality?
Daytona is an agent-agnostic infrastructure middleware upon which OpenHands is built. This means that it provides the underlying framework that enables OpenHands to operate seamlessly, irrespective of the underlying infrastructure. Daytona's capabilities extend to secure sandbox management, effortless scaling, and efficient task allocation, which all contribute to the robust functionality of OpenHands.
How does OpenHands' secure sandbox management work?
OpenHands uses Daytona's secure sandbox management feature to execute code safely. That is, it creates isolated, secure environments where OpenHands can execute code without risking main system resources. This sandbox management functionality ensures that the integrity of the broader system is maintained even when OpenHands is navigating and modifying codebases.
How scalable is OpenHands for large-scale projects?
OpenHands is extremely scalable in handling large-scale projects. Through the assistance of Daytona’s infrastructure middleware, OpenHands can run multiple instances simultaneously to handle larger tasks with greater efficiency. Furthermore, with its ability to handle code refactoring, migration, and troubleshooting tasks, OpenHands is especially useful for large-scale projects with numerous dependencies and workflows.
How does OpenHands facilitate end-to-end work without switching environments?
OpenHands' integrated workspace, complete with an embedded shell, web browser, editor, and task planner, facilitates end-to-end work without the need to switch environments. This means developers can complete a full cycle of tasks, from creation to deployment, in a singular workspace, reducing the need for multiple toolsets and providing a streamlined experience.
How does OpenHands automate repetitive tasks in code development?
OpenHands automates repetitive tasks in code development by using its autonomous navigation and modification capabilities. By identifying patterns and standard procedures, OpenHands takes over such repetitive tasks as testing changes or troubleshooting code issues, relieving human developers of these time-consuming duties and thereby accelerating the code deployment cycle.
How adaptable is OpenHands + Daytona to enterprise needs?
OpenHands, coupled with Daytona, is highly adaptable to enterprise needs. It offers scalability, compliance, and the ability to integrate with existing infrastructure. Its secure and controlled environment is appealing to large organizations in particular, while its ability to understand and respond to natural language instructions makes it accessible to a wide range of users irrespective of their technical expertise.
How does OpenHands navigate and modify codebases autonomously?
OpenHands navigates and modifies codebases autonomously by using inbuilt algorithms that allow it to understand code structure and functionality. It can navigate through different sections of code, identifying dependencies and functions, and can modify or refactor the code as needed to achieve a particular task or resolve any detected issues.
How can OpenHands help in testing and debugging code?
OpenHands helps in testing and debugging code by autonomously exploring codebases, making changes, and validating these changes through testing. If it encounters bugs or errors, OpenHands is capable of troubleshooting and resolving these issues independently, reducing the need for human intervention and quickening the debugging cycle.
What is the capacity of OpenHands for task allocation?
OpenHands leverages Daytona’s efficient task allocation system to manage various tasks. Daytona's infrastructure middleware allows each instance of OpenHands to operate at peak performance by intelligently distributing resources across different tasks, thus ensuring seamless operation and increasing overall efficiency.
How does OpenHands work with Daytona for agent-agnostic infrastructure?
OpenHands, built on Daytona, can operate seamlessly on any underlying infrastructure. This is due to Daytona’s status as an AI agent-agnostic infrastructure middleware. It means that instead of being tied to a specific platform, OpenHands can function effectively across any infrastructure, offering flexibility and adaptability to diverse needs and enterprise-scale projects.
What does it mean that OpenHands can operate seamlessly on any underlying infrastructure?
OpenHands' ability to operate seamlessly on any underlying infrastructure is a direct result of its foundation on Daytona. Daytona, being an agent-agnostic infrastructure middleware, accommodates the complexities of different infrastructures, making sure OpenHands can perform its functions regardless of the specific environment it is deployed in. This ensures a smooth, consistent operation that isn't limited by infrastructure-specific constraints.
What are the security features of OpenHands + Daytona?
OpenHands, in conjunction with Daytona, offers robust security features. This includes secure sandbox management, which allows OpenHands to execute code in isolated environments without compromising the main system resources. The use of Daytona means enterprise-grade security considerations, like staying behind firewalls and controlling access via HTTPS and SSH standards, are integrated into the operation.
How does OpenHands facilitate natural language collaboration between technical and non-technical users?
OpenHands facilitates natural language collaboration by using its natural language processing capabilities to understand and respond to user instructions in a variety of languages. This feature is accessible to both technical and non-technical team members allowing them to assign and receive updates on tasks in real time, fostering a collaborative environment.
 MongoDB - Build AI That Scales
MongoDB - Build AI That Scales